Pinging another device on a local network can be important to determine whether the host is present and not in an indeterministic state (e.g., the processor in a security camera has become unresponsive and no longer triggers on motion). However, not all hosts reply to low level ICMP ECHO ping requests. Therefore, it may be necessary to utilize another form of echo packet or even initiate a layer 4 handshake (e.g., connect on port 80 for an HTTP server). The example Java class Scan provided below provides two ways to scan / ping a host:
- InetAddress.isReachable initiates a traditional ping request when used with the right permissions.
- SocketChannel.connect initiates a TCP handshake / connection.
The purpose of the InetAddress class in the java.net package is to represent, test, and interact with an IP address and the host attached to the address. One of the methods in the InetAddress class is IsReachable. From the JAVA API Specification, the method can be used to...
An alternative to IsReachable is to establish a TCP socket utilizing the InetSocketAddress and SocketChannel classes. This has shown to have similar time delay performances as ping as long as the remote host is listening on the chosen port. For surveillance nodes that typically act as an embedded web server, the use of port 80 (HTTP) can be a good choice and provide good performance (just a few ms of delay).
The section below provides examples and Wireshark test results on MacOS Sierra using Java 8 Update 121 and invoking Scan from the command line. Note that the delays shown in Wireshark and on the command line are not perfectly correlated, so it's up to the implementer to determine which delay is more important when choosing the best approach to scan a host. Note that the results on Ubuntu 16.04 / Linux provide similar results.
Results on Windows are a little different. Invoking Scan in Windows 10 from a power shell will transmit a ping (without running as administrator). In previous releases of Windows and prior versions of Java, multiple TCP echo transmits were witnessed before a success would be returned.
Transmit a TCP SYN packet on port 7 (Echo):
$ java Scan <host> scan using inetAddress.isReachable: responded in 1 ms

Transmit a true ping:
$ sudo java Scan <host> scan using inetAddress.isReachable: responded in 1 ms

Initiate a TCP SYN, ACK, FIN handshake on port 80 (HTTP):
$ java Scan <host> 80 scan using SocketChannel.connect: responded in 5 ms
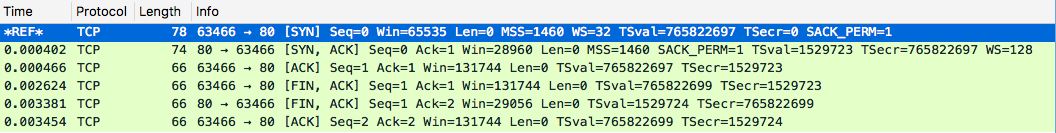
Transmit a TCP SYN packet on port 7 (Echo), but port is down (still in ARP cache). Note that the full transaction now takes seconds
$ java Scan <host> 80 scan using inetAddress.isReachable:Failed

Note that this method can hang for a substantial time if the port is down. However, the performance is similar to the echo request if the destination port is closed (e.g., no web serever configured for port 80).
Transmit a TCP SYN packet on port 7 (Echo) with echo service enabled:
$ java Scan <host> scan using inetAddress.isReachable: responded in 2 ms
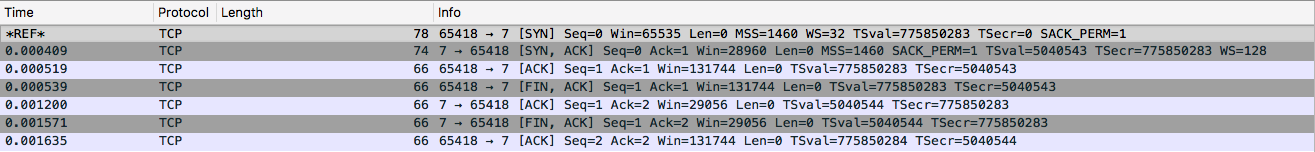
Note, running an echo daemon is not the usual, but you can do it easily with inetd. The following was used to enable echo service on Ubuntu 16.04:
$ sudo update-inetd --verbose --add "echo stream tcp daemon internal internal" Processing /etc/inetd.conf Processing service `echo' ... added Number of currently enabled services: 1 Using tempfile /tmp/inetd... About to send SIGHUP to inetd (pid: 4569) New service(s) added
/*
* Copyright (c) 2017 Mind Chasers Inc.
*
* file: Scan.java
*
* ping / scan another host on your network
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS" AND ANY AND ALL EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
* WARRANTIES ARE DISCLAIMED, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED
* WARRANTIES OF TITLE, MERCHANTABILITY, AGAINST INFRINGEMENT, AND FITNESS
* FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
*
*/
package com.mindchasers;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Date;
public class Scan {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String usage = "java Scan []";
String hostAddress = "";
int port;
long timeToRespond = 0; // in milliseconds
if (args.length < 1 || args.length > 2) {
System.out.println("usage: " + usage);
return;
}
try {
hostAddress = args[0]; // copy the string
if (args.length == 2)
port = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); // convert the integer
else
port = 80;
if (args.length == 1) {
System.out.printf("scan using inetAddress.isReachable:");
timeToRespond = test(hostAddress);
}
else {
System.out.printf("scan using SocketChannel.connect:");
timeToRespond = test(hostAddress, port);
}
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("Problem with arguments, usage: " + usage);
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (timeToRespond >= 0)
System.out.println(" responded in " + timeToRespond + " ms");
else
System.out.println("Failed");
}
/**
* Connect using layer3
*
* @param hostAddress
* @return delay if the specified host responded, -1 if failed
*/
static long test(String hostAddress) {
InetAddress inetAddress = null;
Date start, stop;
try {
inetAddress = InetAddress.getByName(hostAddress);
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
System.out.println("Problem, unknown host:");
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
start = new Date();
if (inetAddress.isReachable(5000)) {
stop = new Date();
return (stop.getTime() - start.getTime());
}
} catch (IOException e1) {
System.out.println("Problem, a network error has occurred:");
e1.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e1) {
System.out.println("Problem, timeout was invalid:");
e1.printStackTrace();
}
return -1; // to indicate failure
}
/**
* Connect using layer4 (sockets)
*
* @param
* @return delay if the specified host responded, -1 if failed
*/
static long test(String hostAddress, int port) {
InetAddress inetAddress = null;
InetSocketAddress socketAddress = null;
SocketChannel sc = null;
long timeToRespond = -1;
Date start, stop;
try {
inetAddress = InetAddress.getByName(hostAddress);
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
System.out.println("Problem, unknown host:");
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
socketAddress = new InetSocketAddress(inetAddress, port);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
System.out.println("Problem, port may be invalid:");
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Open the channel, set it to non-blocking, initiate connect
try {
sc = SocketChannel.open();
sc.configureBlocking(true);
start = new Date();
if (sc.connect(socketAddress)) {
stop = new Date();
timeToRespond = (stop.getTime() - start.getTime());
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Problem, connection could not be made:");
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
sc.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return timeToRespond;
}
}





